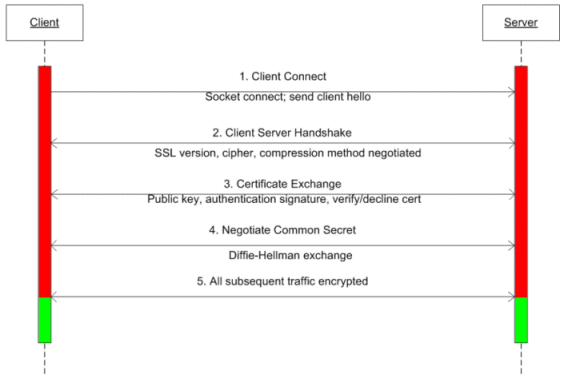
The key to understanding how SSL works is to understand the elements that take part in the process. A key element of SSL is the SSL certificate. A public-key certificate, usually just called a certificate, is a digitally-signed document that ties the value of the public-key to the identity of the server service that holds the corresponding private key.

Typically, a certificate contains the following information:
The server’s public key value, which the clients use to encrypt a session key (The client and the server use the session key to encrypt data). This public-key does not exist as a file, but rather is produced when a certificate and private key are created.
The server’s identifier information, such as the name, e-mail address, common domain name, and other details.
The validity period (the time that the certificate is considered valid)
Issuer or signer identifier information
The digital signature of the issuer, which attests to the validity of the binding between the server public key and the organization's identifier information.
There are many certificate types or standards, with the Server supporting the most common ones. The Server can import into its certificate store any client-provided certificate of type PKCS 7 or 12, and the X.509 DER encoded standard. For the certificate that the server itself provides (to the connecting client during the SSL handshake), it supports X.509 and PKCS #12 only. Note that PKCS #12 embeds both the certificate AND private key into a single file. The default type that is created by EFT Server is x.509 base-64 standard DER encoded.
Before a certificate can be used for securing connections, it must be created (generated) and signed (or vouched for). Certificates can be created directly from EFT Server, or by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA), which is an independent and trustworthy entity responsible for issuing and managing digital certificates, including revocation of certificates that are expired or are otherwise unauthorized. Once created, a certificate should be signed. By digitally "signing" a newly issued certificate, the signer guarantees the authenticity of the data held in the signee’s certificate. The Server can sign its own certificates; however, it is recommended that the certificate be signed by a trusted 3rd-party CA.
When generating a new certificate, the Server creates a self-signed certificate and a certificate signing request (or CSR) file that you can send to a CA for signing and then import into EFT Server.
Files created by EFT Server:
Private key file (.key) - The private key should never be distributed to anyone. It is used to decrypt the session that is encrypted by the public key.
Certificate request file (.csr) - Each time you create a certificate using the Server, a Certificate request file is also created. This file can be signed by the Server's Certificate Signing Utility or sent to intermediate certificate authority such as GeoTrust, Verisign (www.verisign.com), or Thawte (www.thawte.com) for signing.
Certificate file (.crt) - This is a self-signed certificate. To obtain a 3rd-party signed certificate, you must send the certificate signing request file to a Certificate Authority (CA) such as Verisign, Geotrust, or Thawte. The CA in turn will send you a new .crt file with which you can replace your self-signed one.
Trust in a certificate is established when you have a copy of the signing certificate in your certificate store (for example, the Server’s store or Internet Explorer's Trusted Root Certification Authority for clients). The certificate does not necessarily have to be signed by a root CA; it can be signed by subordinate intermediate CA, as long as there is a valid certification path from the signing certificate to a trusted root certificate, meaning that none of the certificates in the certification path have been revoked or is expired.
|
|
The Server supports one level of trust when requiring certificates from connected SSL clients. That is, if certificate A is trusted, then certificate B signed by certificate A is also trusted. However, if certificate C is signed by certificate B, then certificate C is not trusted. |