|
General Tab Parameters |
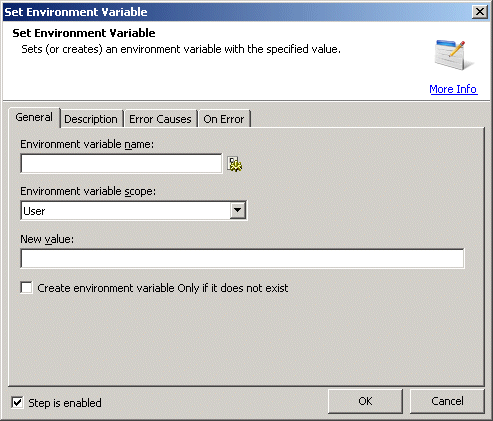
Environment variable
name: Specifies the name of the environment variable to set.
Text, Required
MARKUP: NAME="Temp"
Environment variable
scope: Specifies the scope of the environment variable. The available
options are:
User
- The environment variable is stored or retrieved from the HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment
key in the Windows operating system registry. When the user creates the
environment variable in a set operation, the operating system stores the
environment variable in the system registry, but not in the current process.
If the user starts a new process, the operating system copies the environment
variable from the registry to that process. When the process terminates,
the operating system destroys the environment variable in that process.
However, the environment variable in the registry persists until the user
removes it using a program or by means of an operating system tool.
Machine
- The environment variable is stored or retrieved from the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session
Manager\Environment key in the Windows operating system registry. When
a user creates the environment variable in a set operation, the operating
system stores the environment variable in the system registry, but not
in the current process. If any user on the local computer starts a new
process, the operating system copies the environment variable from the
registry to that process. When the process terminates, the operating system
destroys the environment variable in that process. However, the environment
variable in the registry persists until a user removes it using a program
or by means of an operating system tool.
Text [options], Optional - Default "User"
MARKUP: TYPE="User"
New value: Specifies
the new value of the environment variable.
Text, Required
MARKUP: VALUE="C:\Documents and Settings\Users\Temp"
Create environment
variable Only if it does not exist: Specifies whether or not to
create a new variable if it does not exist.
If you select the check box
(Yes) and a variable with the same name exists, the system generates an
error saying that the environment variable already exists. If the variable
does not exist, it creates it. If you clear the check box
(No) and a variable with the same name exists, then the system would overwrite
its value with the one given by the user. If the variable with the same
name does not exist, the system creates a new one.
Yes/No, Optional - Default "No"
MARKUP: CREATEIFNOTEXIST="YES" |

