GlobalSCAPE Secure FTP Server, v3 Quick Start Guide
The topics below provide instructions for installing and configuring Secure FTP Server and its SFTP module, and configuring Windows to interoperate with Cisco CUCM versions 5.1 and 6.1 with Secure FTP Server. Follow the steps in order as described in this guide.
-
Install the Server and the SFTP module and Activate Secure FTP Server.
-
Configure CUCM to transfer data using Secure FTP Server
For more information about GlobalSCAPE's Secure FTP Server, visit http://www.globalscape.com/gsftps/.
For instructions for adding user accounts and other Secure FTP Server configuration procedures, refer to the in-application help or the online help at http://help.globalscape.com/help/secureserver3/.
Download the Secure FTP Server software and the SFTP module on GlobalSCAPE's download page, at http://www.globalscape.com/downloads/gsftps.aspx.
To install Secure FTP Server
-
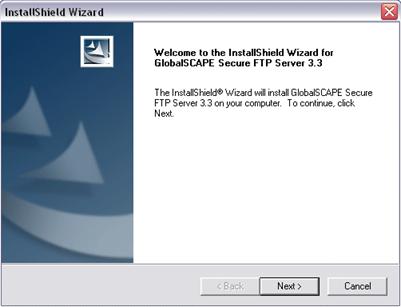
Double-click the executable to start the installer. The Welcome page appears.
-
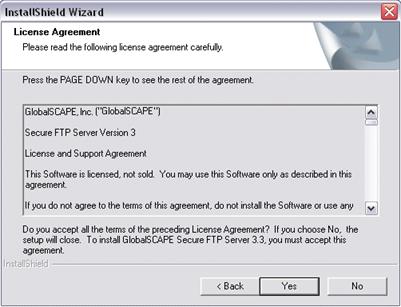
Click Next. The License Agreement appears.
-
You must read and then accept the license agreement (click Yes) in order to continue.
-
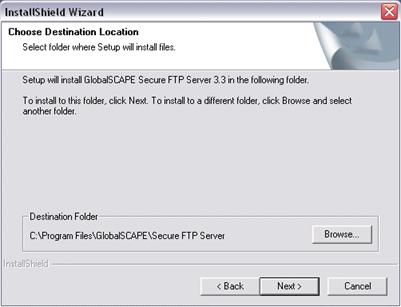
Click Next. The Destination Location page appears.
-
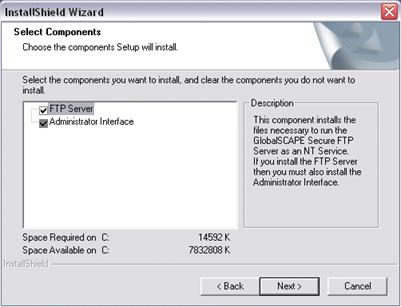
Specify the folder in which to install Secure FTP Server, then click Next. The Select Components page appears.
-
FTP Server: This component installs the Server that runs as an NT Service.
-
Administrator Interface: This component is the administrative interface for the server. It must be installed on the server machine and it may be installed on a separate machine to provide remote administration over TCP/IP.
-
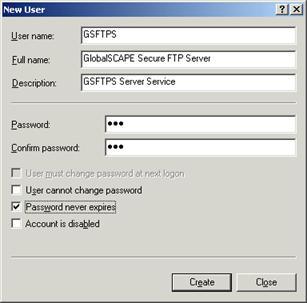
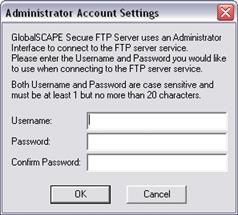
Click Next. The Administrator Account Settings page appears.
-
Create a username and password that you will use to connect to and administer Secure FTP Server, then click OK.
-
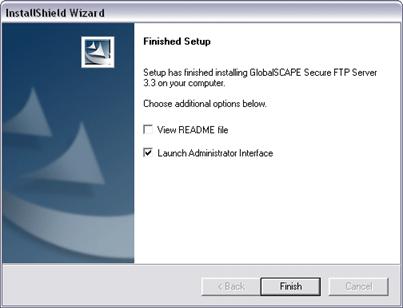
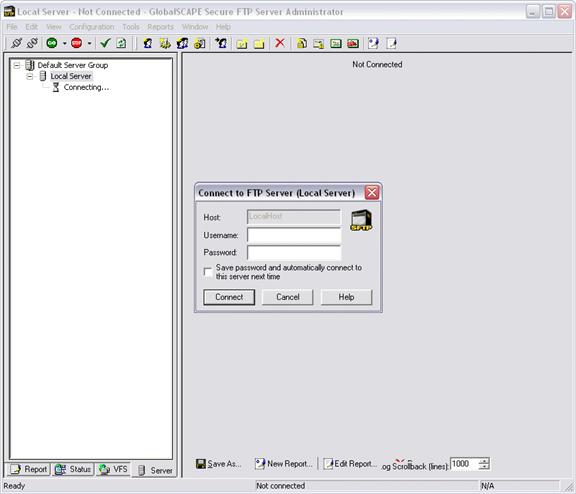
The Launch Administrator Interface check box is selected by default. Select the View README file check box if you want to read the release notes, then click Finished. The GlobalSCAPE Secure FTP Server Administrator and Connect to FTP Server dialog box appear.
-
Provide the administrator Username and Password that you created during installation, then click Connect. The Welcome dialog box appears.
-
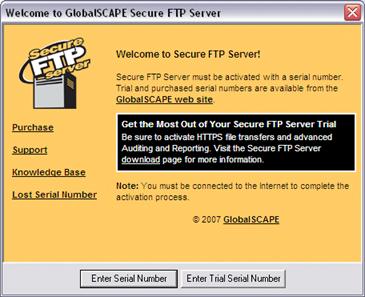
If you are evaluating the software, a trial serial number is needed to continue. If you have not already received a trial serial number, you can request one on the GlobalSCAPE support pages. Click Enter Trial Serial Number and follow the instructions.
-
If you have purchased the software, click Enter Serial Number and follow the instructions.
-
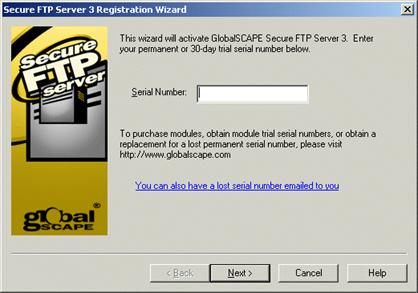
Type or paste your serial number in the Serial Number box, then click Next. The Personal Details page appears.
-
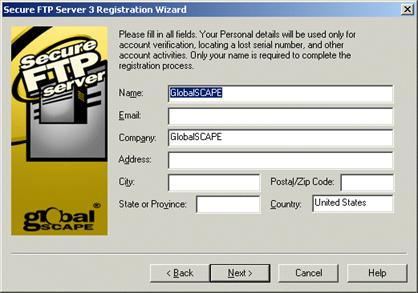
The information on this page can be used to verify your account if you need to contact Customer Support. Complete the personal details fields, then click Next. Registration of the Server is complete.
-
Click Finish. The Create New Site wizard appears.
-
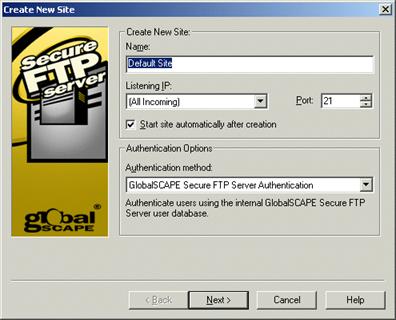
Provide a Name for the Site or keep the default name. This name will appear in the Server tree.
-
Click the Listening IP list, then click the address of the computer or keep the default of All incoming.
-
In the Port box, type or select the port number. The default port used for FTP connections is 21, however, you can enter any value between 1 and 65,535. (If you are using the site for secure FTP connections, you can later turn off plain FTP access on the Connection Options tab.)
-
The FTP connection to the Server is called a Site. If you want the connection to be available immediately, select the Start site automatically after creation check box. Otherwise, you can clear the check box and start the Site later.
-
Specify the Authentication method. The default method is GlobalSCAPE Secure FTP Server Authentication. GlobalSCAPE Authentication does not rely on outside sources for user information. All information in the authentication database is protected from the operating system, contained within the .aud file located in the Server installation folder, and encrypted, and can only be modified through the Administrator
-
If you need to use NT Authentication see Creating a site that uses NT authentication.
-
If you need to use ODBC authentication, see Creating a site that uses ODBC authentication.
-
Click Next. The Authentication Options page appears.
-
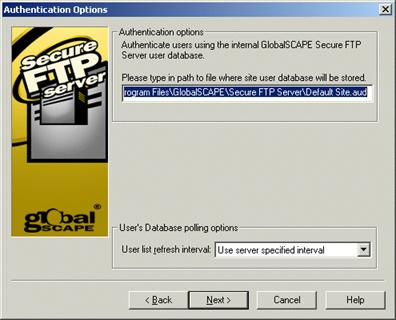
Provide the path at which to store the user database. Leave the default path unless you want to store the authentication database in a new location.
-
In the User list refresh interval list, specify how often the Server should check the authentication database for new users (Never, every 5, 15, or 30 minutes, 1, 2, 6, or 12 hours, or once per day).
-
Click Next. The final page of the wizard appears.
-
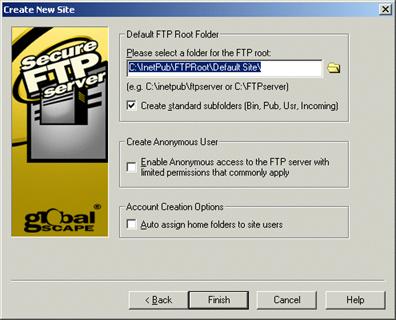
In the Default FTP Root Folder area, specify a path to the root folder for the site.
-
Select the Create standard subfolders check box to automatically create Bin, Pub, Usr and Incoming folders with appropriate permissions under the root folder. This is selected by default, but is only necessary if you are trying to mimic a typical default *nix Server setup.
-
Select the Enable anonymous access to the server check box to create an anonymous account that does not require a password. The account will have limited permissions.
-
Select the Auto assign home folders to site users check box to automatically create a user folder under \Site Root\Usr\ when a new user is added.
-
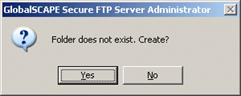
Click Finish. If the root folder has not already been created, you are prompted to do so.
-
Click Yes. The folder is created and the Create New Site wizard closes.
The FTP Server and Administrator Interface check boxes are selected by default.
|
|
If the administrator username or password is lost, you will not be able to administer the Server. Resetting the administrator account is possible, but will result in the loss of all user and group specific settings.. |
The Server service and Administrator interface are installed and the Finished Setup page appears.
The Registration wizard appears.
|
|
Assigning port numbers under 1024 may lead to conflicts with other programs running on your computer. |
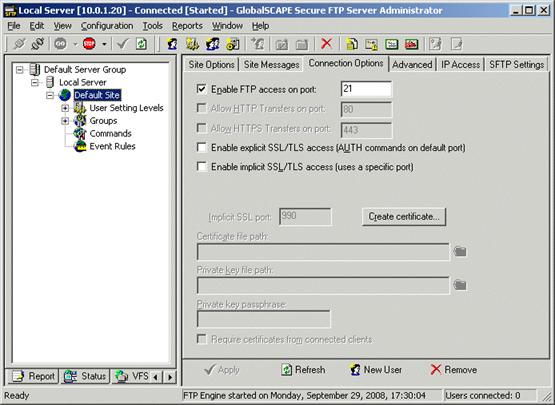
Secure FTP Server is now configured to allow FTP connections at the IP address and port that you specified.
|
Next: Activate the SFTP module so that you can configure it to allow the Site to use SFTP to connect to Secure FTP Server. |
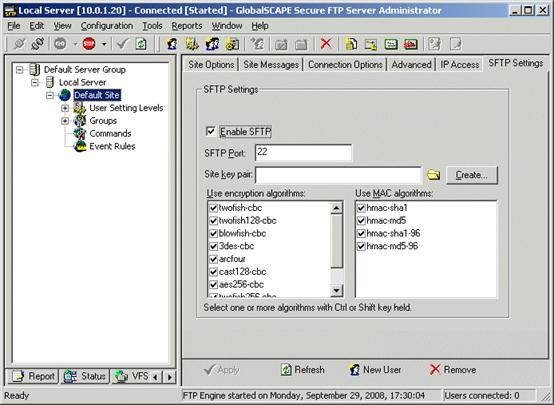
The SFTP module requires the purchase of an SFTP module license.
To activate the module
-
On the main menu, click Help > Enter SFTP Module Serial Number.
-
Follow the instructions in the wizard to activate the module. (Refer to the procedure for activating the Server, if necessary.)
The Registration Wizard appears.