File and Folder Properties
Just as in Windows Explorer, you can view the properties of any file or folder by right-clicking the file, then clicking Properties.
Local pane information:
-
Type: Kind of item (e.g., HTML document, File Folder)
-
Location: Path where the file resides (e.g., C:\Documents and Settings\user1\My Documents; on the remote server, displays the directory)
-
Opens with: Indicates in which application the file opens. To open ALL files of that type with a different application, click Change. For example, if your computer is configured to open GIF (image) files in Internet Explorer, but you want them to open in Paint Shop Pro so that you can edit them, click Change, scroll to or browse for psp.exe, then click OK. This change will affect ALL files on your computer that have that extension.
-
Size: Size of the file or folder (e.g., 43.1 MB (45,281,728 bytes))
-
Contains: For folders, displays how many files and subfolders it contains
Remote pane information:
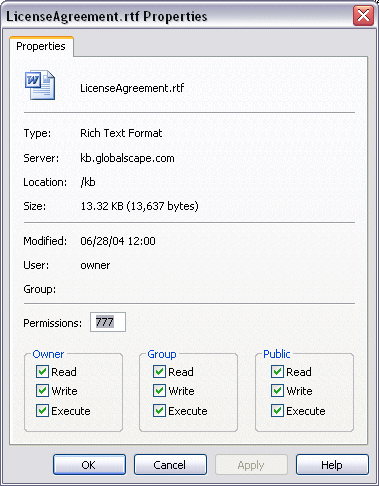
-
Server: The address (URL) of the server on which the file resides
-
Modified: When the item was last modified
-
User: Specifies the user of the item (e.g., owner)
-
Group: Specifies the group to which the item belongs (can be blank)
-
Read/WritePermissions: You can set the CHMOD permissions by changing the number (such as 777), or just check off the permissions in the Owner, Group, and Public area of the dialog box.
About CHMOD Permissions
The CHMOD permission mask is a three-digit number.
-
First digit: Defines the permissions for the owner (you).
-
Second digit: Defines the permissions for the group.
-
Third digit: Defines the permissions for everyone else (referred to as public).
Each digit works the same for each group of users: the owner, group, and public. What you set for one digit has no effect on the other two digits. Each digit is made up of the three Read, Write, and Execute permissions. The Read permission value is 4, the Write permission value is 2, and the Execute permission value is 1. These three numbers are added together to get the permissions for a file. If you want a file only to be readable and not writable or executable, set its permission to 4. This works the same for Write and Execute. Executable only files have a permission of 1.
For example, if you want a file to have Read and Write permissions, add the Read and Write values together (4+2) and you get 6, which is the permissions setting for Read and Write. If you want the file to have Read, Write, and Execute permissions, use the value 7 (4+2+1). Do this for each of the three permission groups and you get a valid CHMOD mask. If you want your file to have Read, Write, and Execute permissions (4+2+1) for yourself; Read and Execute (4+1) for your group; and Execute (1) only for everyone else, you would set the file permissions to 751. (Or just select the appropriate check boxes under Owner (you), Group, and Public.)