Connecting to EFT from Outlook
Typically, the EFT Outlook Add-In server connection information is configured by the administrator. You should not edit these settings unless directed to do so by your administrator. EFT administrators should also refer to Configure a Service Principal Name SPN for Windows Authentication, below, to configure Integrated Windows Authentication (Kerberos).
You might want to edit these settings are if your username/password has changed, if the server is moved to another host, if your login type was changed, or if you need to change the log file location.
If the EFT Outlook Add-In is not connected to the server, it will not try to upload packages.
In the General Configuration dialog box, accessed from the EFT Outlook Add-In toolbar/ribbon, you can specify to which server you want to connect, how to authenticate your connection, and where to save log files. In most cases, your administrator will configure this for you during setup.
To configure the EFT Outlook Add-In
-
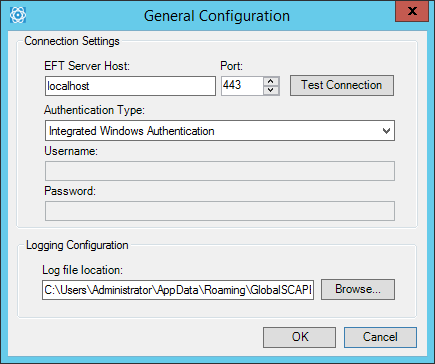
On the EFT Outlook Add-In toolbar/ribbon, click General Configuration. The General Configuration dialog box appears.
-
In the EFT Server Host box, provide the host name of EFT.
-
In the Port box, provide the port used by EFT for HTTPS connections.
-
In the Authentication type box, specify either manual or Windows authentication:
-
Manual—You must provide the username and password that you use to connect to EFT or your AD credentials.
-
In the Username box, provide the username that you use to connect to EFT or your AD username.
-
In the Password box, provide the password that you use to connect to EFT or your AD password.
-
Integrated Windows Authentication—Used this login type if you connect to EFT via Single Sign On (Kerberos). In this case, you do not need to provide a username and password. Your Windows credentials are used to connect.
-
If you want to test your connection, click Test Connection.
-
(Optional) In the Log file location box, specify the path at which the log file is saved.
-
Click OK to save your changes, or click Cancel if you do not want to save your changes.
Use the EFT login credentials for the EFT user account, not the administrator.
Configure a Service Principal Name (SPN) for Windows Authentication
Use this topic as a checklist to correctly configure the Outlook Add-In so that users can authenticate with EFT using integrated Windows Authentication.
Why do I need an SPN? According to Microsoft Technet, "A service principal name (SPN) is the name by which a Kerberos client uniquely identifies an instance of a service for a given Kerberos target computer. If you install multiple instances of a service on computers throughout a forest, each instance must have its own SPN. A given service instance can have multiple SPNs if there are multiple names that clients might use for authentication. For example, an SPN always includes the name of the host computer on which the service instance is running, so a service instance might register an SPN for each name or alias of its host."
Using the Windows "setspn" utility, create the Service Principal Name (SPN), which is necessary for Kerberos to function correctly for EFT. The SPN is a name by which the Add-In can uniquely identify the EFT Server service.
The “setspn” utility is typically installed by default on Active Directory server computers. The command must be run using an account with Active Directory administration rights. Typically it is easiest to perform these steps on the domain’s primary Active Directory server.
To create the SPNs, execute the following at a command prompt:
setspn –A HTTP/eftserver eftpreauthuser
setspn –A HTTP/eftserver.globalscape.local eftpreauthuser
setspn –A HTTP/eftserver.globalscape.com eftpreauthuser
Where:
-
eftserver eftpreauthuser is the host name of the computer running EFT; the host name that workstations would use internally to communicate with the EFT computer.
-
eftserver.globalscape.local eftpreauthuser is the fully qualified host name of the computer running EFT; the full host name that workstations would use internally to communicate with the EFT computer.
-
eftpreauthuser with the username of Active Directory domain account used in the “KDC pre-auth username” field of the EFT Kerberos Configuration.
-
eftserver.globalscape.com is the address to which the Add-In will connect.
Do not type "HTTP://" -- the proper prefix is "HTTP/"
These SPNs should work regardless of the account the EFT server service is running as.
If duplicate SPNs exist (meaning multiple domain accounts with the same HTTP/<SPN>), then Kerberos will not work correctly. Once the SPN has been associated with the Kerberos Pre-Auth Account used by EFT to participate in Kerberos Authentication, you can double-check for duplicate SPNs on the domain using the command: setspn –X.
To view the SPNs to verify that they were created successfully, run the following command after substituting <PreAuthUsername> auth user account:
setspn –l <PreAuthUsername>
(Note: The switch is a lower-cased letter L, not the number one.)