SNMP Preferences
Use the SNMP subsection of the Server Preferences section to set the default SNMP settings for each SNMP access method. These settings are used for all new devices.
About SNMP Versions
InterMapper can retrieve data from devices using SNMP version 1, version 2c, or version 3. Each of these can access the same SNMP information, but through different means:
- SNMPv1 was the original version, and provided a simple means for retrieving data. Security was provided through community strings that acted like a password to allow or deny access to the information. The Read-Only community string gave permission to the requester to read data; the Read-Write community string gave permission to modify data. All data transmissions (including the community string) were sent "in the clear", that is, unencrypted.
- SNMPv2c provided additional, more efficient methods to request data, and added new data types (such as 64-bit counters) so that the monitoring system could get more accurate data. SNMPv2c is like SNMPv1 in that it uses the same community string system, and transmits data in the clear.
- SNMPv3 provides the same data retrieval facilities as SNMPv2c, with additional security. There is a secure method of providing authentication information (so the device knows whether to respond to the query or not), as well as a privacy function that encrypts the entire transmission so that eavesdroppers cannot discern the data.
What is an SNMP Community String?
The SNMP Read-only Community string is like a user id or password that allows access to a router's or other device's statistics. InterMapper sends the community string along with all SNMP requests. If the community string is correct, the device responds with the requested information. If the community string is incorrect, the device simply ignores the request and does not respond.
Note: SNMP Community strings are used only by devices which support SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c protocol. SNMPv3 uses username/password authentication, along with an encryption key.
Community String Types
There are actually three community strings for SNMPv1-v2c-speaking devices:
- SNMP Read-only community string - enables a remote device to retrieve "read-only" information from a device. InterMapper uses this information from devices on its maps.
- SNMP Read-Write community string - used in requests for information from a device and to modify settings on that device. InterMapper does not use the read-write community string, since it never attempts to modify any settings on its devices.
- SNMP Trap community string - included when a device sends SNMP Traps to InterMapper. InterMapper accepts any SNMP Trap community string.
By convention, most SNMPv1-v2c equipment ships from the factory with a read-only community string set to "public". It is standard practice for network managers to change all the community strings so that outsiders cannot see information about the internal network. (In addition, network managers may employ firewalls to block any SNMP traffic to ports 161 and 162 on the internal network.)
SNMP Server Settings Pane
InterMapper remembers the default settings for each of the various SNMP
access methods. These are set in the Server Settings>SNMP preference
pane. 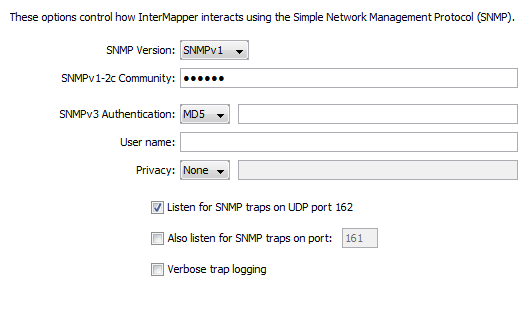
This pane allows you to specify the following:
Setting the default SNMP preferences
- SNMP Version - Select the default SNMP version to be used for new devices in autodiscovery. InterMapper will attempt to use the selected version when it discovers a new device. If it gets a response, it will continue to use that version. If that fails, then it will simply ping the device.
- SNMPv1-2c Community - If the selected SNMP Version is either SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c, InterMapper will use this community string to attempt to communicate with the device.
- SNMPv3 Authentication - If the selected SNMP version is SNMPv3, InterMapper will use the specified authentication method (SHA, MD5, or None) with the indicated password on the right to authenticate with the device.
- User Name - The SNMPv3 user name to be used for authentication and privacy.
- Privacy - When using SNMPv3, the privacy method (DES, AES, or None) will be used with the encryption password on the right.
- Listen for SNMP Traps on UDP Port 162 - Check this box if you want InterMapper to listen for SNMP traps sent from devices to the standard port 162.
- Also listen for SNMP traps on UDP port - InterMapper can listen for traps on a second, non-standard port (in addition to port 162). Check this box and enter the port number in the text box. Traps received on this alternate port are handled in the same manner as those received on port 162.
- Verbose trap logging - Check this box to instruct InterMapper to display the full OID and contents for all varbinds of a trap, instead of simply the varbind contents.
Setting SNMP Preferences for Specific Devices
The panel shown above sets the default SNMP preferences that InterMapper uses when querying devices. You can also set SNMP preferences for individual devices on your map using the Set Community... (SNMPv1-v2c) or Set Probe... (all three SNMP versions) commands, available from the Monitor menu. You can set various parameters for one or more devices at a time, by selecting the devices you want to change before executing the command.