Installing Intermapper on Debian and Ubuntu Linux Systems
Intermapper is shipped as a Debian package (.deb file) and is available in 64-bit: intermapper_6.6.4-18.04-1_amd64.deb. This includes Intermapper server and Intermapper Flows server.
The Debian package can be installed using the system's graphical package manager, from a command line, or using apt-get.
Along with the adoption of SystemD for management of Intermapper services, Intermapper for Linux has been updated to conform to the Linux File System Hierarchy Standard’s policy for packaged applications. For Intermapper 6.6 or higher, the default installation root directories are as follows:
| Files | New default installation root directory | Previous default installation root directory |
|---|---|---|
| Intermapper Program files | /opt/helpsystems/intermapper | /usr/local |
| Intermapper Data files | /var/opt/helpsystems/intermapper | /var/local |
The installer creates a link (typically in the directory /usr/local/bin) to ensure that you can start Intermapper UI by issuing the command intermapper at the shell prompt. The path /usr/local/etc/intermapperd.conf continues to be reserved – it is now a link to the actual configuration file.
A compatible Java JRE is automatically installed with each version of Intermapper server. This file runs the Intermapper client.
Installing from a command line
Run the following command:
sudo dpkg -i "intermapper_6.6.4–18.04-1_amd64.deb"Installing Intermapper using apt
-
Add the repository URL to the /etc/apt/sources.list file:
Copyecho "deb [trusted=yes] https://hsdownloads.helpsystems.com/intermapper/debian /" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.listAfter you import the key, apt remembers it for future releases. You do not need to import it again.
-
Add the GPG key used for signing to APT's keyring using Ubuntu's suggested method:
Copysudo apt-key adv --fetch-keys https://hsdownloads.helpsystems.com/intermapper/debian/fortra-release-public.asc | sudo tee /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/hsdownloads.helpsystems.com.asc -
Run the installation command:
Copysudo apt update && sudo apt install intermapper
Removing an old or expired Intermapper Release Signing Key
If the Intermapper Debian Repository Release Signing Key is no longer used or expired, Fortra recommends stop using the old key and remove it from the apt keyring.
To do so, find the fingerprint for the key you wish to delete by listing all keys in the apt keyring using the following command:
sudo apt-key listThe following is an example of the output:
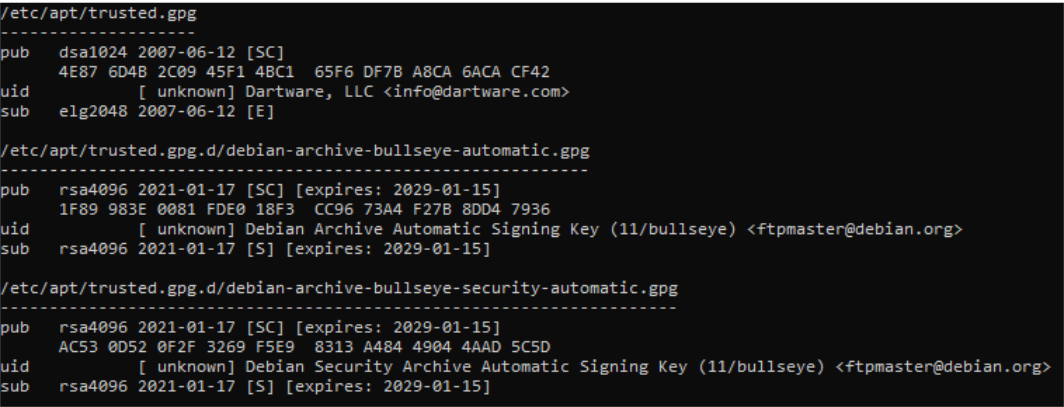
Remove the old info@dartware.com public key whose fingerprint is 4E87 6D4B 2C09 45F1 4BC1 65F6 DF7B A8CA 6ACA CF42.
Using the last eight characters of that fingerprint, delete it with the following command:
sudo apt-key del 6ACACF42Upgrading Intermapper
When you upgrade an existing Intermapper installation to a newer version, you do not lose data in the InterMapper Settings folder. Fortra recommends that you create a backup of that folder before you upgrade. For information on which files to back up, see What is Installed and Where.
Upgrading from a command line
You can install the upgrade package using the following command:
cd <directory-containing-deb>
sudo dpkg -i "intermapper_6.6.4-18.04-1_amd64.deb"On some versions of Ubuntu, you must remove old 32-bit packages using the following commands before you install the new 64-bit package:
cd <directory-containing-deb>
sudo dpkg -r intermapper:i386
sudo dpkg -r intermapper-datacenter:i386If you are upgrading from version 5.7 or earlier, contact Fortra Support.
When you start the new Intermapper version, it uses the old configuration.
Starting Intermapper
The Intermapper user interface is launched by executing the command intermapper. The installation process creates a link to that command in the directory /usr/local/bin - provided that the directory exists. To start the Intermapper UI, issue the command /usr/local/bin/intermapper. If that path does not exist, the path at which the link has been created can be seen in the output of the installation command and that path should be used instead.
During installation, /usr/bin/local/intermapper is created if /usr/local/bin already exists, otherwise /opt/local/bin exists, then /opt/local/bin/intermapper is created.
If you cannot run the command above, see Installing Remote Access.
Starting Intermapper Flows
Intermapper Flows Intermapper Flows is installed automatically with Intermapper. It allows you to obtain deeper insight into the traffic on your network. When Intermapper Flows first starts, it creates a 10 GB flows database. You can change the database size and location to fit your needs. Intermapper Flows does not run by default. Use the Intermapper Control Center to start it to access flows information.
Consider the following before starting Intermapper Flows:
- If you are running a trial version, Intermapper Flows is fully operational. After your trial expires, an Intermapper Flows license is required.
- Remove any firewalls on the selected UDP ports for NetFlow. The default port is 2055. NOTE: The Intermapper Flows service/daemon might not start if another program is using port 2055 (or whatever port you have designated for netflow packets). Stop or uninstall other netflow packages on the system.
Intermapper Flows does not include a graphical user interface. However, you can access flow information either through the built-in Intermapper client or through Intermapper RemoteAccess. Open the Flows window by right-clicking a device on a map. When you do this, you can see information about the traffic on the selected device.
If you purchased Intermapper with Flows, use the serial number to register your installation. If you are only trying Intermapper out, your evaluation serial number allows you to receive data from one exporter source (NetFlow or sFlow data).
See the Intermapper User Guide or online help for more information on Intermapper Flows.
Starting Intermapper Flows
You do not need to configure Intermapper DataCenter if you access it from the local machine. To enable external access and more advanced configuration, go to https://localhost:8182.
Intermapper DataCenter ships with a self-signed SSL certificate. Your browser displays a certificate warning when you visit the DataCenter web interface. You can select the certificate and safely continue to navigate to the page. The Intermapper DataCenter Settings page allows you to upload your own certificate rather than relying on the less secure certificate shipped with Intermapper.
What is installed and where
Intermapper components are installed as separate services. This means that after you start them, they automatically begin running when your computer starts, before any users are logged in, and continue running even when no user is logged in. For information on managing these services, see Managing Intermapper Services.
The installer creates files and folders at the following (default) locations:
| File Path |
Contents |
|---|---|
| /var/opt/helpsystems/intermapper/InterMapper_Settings | Intermapper settings |
| /opt/helpsystems/intermapper/bin/ | Intermapper Server binaries |
| /opt/helpsystems/intermapper/bin/intermapperd | Intermapper Server executable |
| /opt/helpsystems/intermapper/bin/intermapperauthd | Intermapper authorization delegate |
| /opt/helpsystems/intermapper/bin/intermapperflows | Intermapper Flows server |
| /opt/helpsystems/intermapper/man/man1/intermapperd.1 | Documentation |
| /opt/helpsystems/intermapper/man/man1/intermapperauthd.1 | Documentation |
| /opt/helpsystems/intermapper/share/intermapper | Intermapper support files |
| /opt/helpsystems/intermapper/imdc | Intermapper DataCenter folder |
| /var/opt/helpsystems/intermapper/InterMapper_Settings/Flows | Intermapper Flows folder |
| /var/opt/helpsystems/intermapper/InterMapper_Settings/Flows/SESSIONDB | Default directory for the flow database |
| /var/opt/helpsystems/intermapper/InterMapper_Settings/Flows/flows.conf | Configuration file for Intermapper Flows |
| /var/opt/helpsystems/intermapper/InterMapper_Settings/Flows/services | List of port numbers and service names |
| /opt/helpsystems/intermapper/share/intermapper/imflows_configure.sh | The IMflows configuration script |
When Intermapper first starts, the Intermapper_Settings folder is created and stored in the /var/opt/helpsystems/intermapper/Intermapper_Settings folder. This folder stores preferences, maps, and data that Intermapper collects from your network. You can change the location of the InterMapper Settings folder by editing Intermapper's configuration file (intermapperd.conf) to which a link is created from the /usr/local/etc folder.
The installer also creates a new folder /opt/helpsystems/intermapper/imdc that contains the Intermapper DataCenter's files, including data and configuration files.
There are now three Intermapper services (intermapperd, imflows, and imdc), managed by systemd on all Linux systems, that have systemd active at the time Intermapper is installed. The systemd service files are located in the /opt/helpsystems/intermapper/share/intermapper/units directory. These files are copied to the appropriate run-time location during the installation process. The SystemV-style startup scripts (as used in earlier Intermapper versions) are supplied in the /opt/helpsystems/intermapper/share/intermapper/sysv.init directory. These files are only installed if systemd is not managing the Linux host when Intermapper is installed.
The intermapperauthd file is a setuid-root program. The intermapperd service (running as a non-privileged user) makes requests to intermapperauthd to access low-level network services, such as ICMP ping and low-numbered network ports.
The installer creates user and group entries named "intermapper" on your system, if they do not exist already. The new user and group configuration and log files are stored in the InterMapper Settings and Intermapper DataCenter folders. These log and configuration files are not granted public read access. If you want to read these files, add yourself to the intermapper group or use sudo in your commands.
Managing Intermapper Services
To start individual services, run the following service management commands:
sudo systemctl start intermapperd.service
sudo systemctl start imdc.service
sudo systemctl start imflows.service To stop individual services, run the following service management commands:
sudo systemctl stop intermapperd.service
sudo systemctl stop imdc.service
sudo systemctl stop imflows.serviceTo verify the version of Intermapper that is installed, run the following command:
/opt/helpsystems/intermapper/bin/intermapperd -vTo check if Intermapper services are currently running, run the following commands:
systemctl status intermapperd.service
systemctl status imflows.service
systemctl status imdc.serviceIntermapper Data Center
You do not need to configure Intermapper DataCenter if you access it from the local machine. To enable external access and more advanced configuration, go to https://localhost:8182.
Intermapper DataCenter ships with a self-signed SSL certificate. Your browser displays a certificate warning when you visit the DataCenter web interface. You can select the certificate and safely continue to navigate to the page. The Intermapper DataCenter Settings page allows you to upload your own certificate rather than relying on the less secure certificate shipped with Intermapper.
Setting a password for the Intermapper Data Center
The Intermapper DataCenter configuration page, accessed from a browser, requires its own password.
Run the following commands:
sudo systemctl stop imdc.service
sudo /opt/helpsystems/intermapper/imdc/sbin/imdc --password=[password]
sudo systemctl start imdc.serviceNow you can connect to Intermapper using one of the following URLs:
Uninstalling Intermapper
To uninstall Intermapper from your system, use the system's graphical package
manager,
sudo dpkg -r intermapperWhen you uninstall Intermapper, the settings and data files are not removed. If you do not plan on reinstalling Intermapper and want to remove it completely,
manually remove the InterMapper Settings, Intermapper Flows,
and Intermapper DataCenter folders
sudo dpkg --purge intermapper
sudo rm -rf /var/opt/helpsystems/intermapper/InterMapper_Settings
sudo rm -rf /opt/helpsystems/intermapper/imdc
sudo deluser intermapperInstalling Remote Access
To install Intermapper RemoteAccess:
Double-click the Intermapper_RemoteAccess_6.6.4.dmg file to open the disk image. Drag the Intermapper RemoteAccess icon into the Applications folder or onto your Desktop. Double-click the icon to start Intermapper RemoteAccess.
If your Intermapper server does not have a graphical interface, use Intermapper RemoteAccess to administer the Intermapper server. Before the Intermapper server can accept connections from Remote Access, launch the server with a command line argument, telling it where to connect from. Run the following commands to manually stop intermapper, grant remote access to the server, and restart Intermapper:
sudo /usr/local/share/intermapper/Stop.sh
sudo /usr/local/bin/intermapperd -f /usr/local/etc/intermapperd.conf --setenv 'Admin=remote:password@*.*.*.*'
sudo /usr/local/share/intermapper/Start.sh
The --setenv Admin "remote:password@*.*.*.*" option tells Intermapper server to accept administrator connections from any IP address (*.*.*.*) with the user ID of remote and the password of password. After you restart the server, launch Intermapper RemoteAccess on another computer, log into the Intermapper server to set up the Admin user with a strong password, and set the allowed addresses for the remote server access list.
The Linux Intermpper RemoteAccess package (a self-extracting installer) does not deliver a Java JRE: it will attempt to use the JRE supplied with an Intermapper Server installation on the same host, or, failing that, a Java Runtime from the host environment.
To start the Intermapper RemoteAccess installer, run the following command:
$ sh ./Install_InterMapper_RemoteAccess_.binTo launch Intermapper RemoteAccess, run the following commands:
$ cd InterMapper_RemoteAccess_
$ ./intermapper_remoteaccess.shIf your Intermapper server does not have a graphical interface, use Intermapper RemoteAccess to administer the Intermapper server. Before the Intermapper server can accept connections from Remote Access, launch the server with a command line argument, telling it where to connect from. Run the following commands to manually stop the intermapperd process, grant remote access to the server, and restart the intermapperd process:
sudo systemctl stop intermapperd.service
sudo /opt/helpsystems/intermapper/bin/intermapperd -f /usr/local/etc/intermapperd.conf --setenv 'Admin=remote:password@*.*.*.*'
sudo systemctl start intermapperd.serviceThe Intermapper RemoteAccess package includes and installs a compatible JRE which runs the Intermapper client.
Silent installation with an ISS file
To silently install Intermapper Remote Access, you must create and use an ISS file.
-
Launch the following as an Administrator from a command line or from a script:
CopyInterMapper_RemoteAccess_Setup_664.exe /s /a /r /f1"c:\temp\imra_setup.iss" -
Continue with the rest of the installation.
Ensure you click the agreement when you run the command and finish the installation.
-
Confirm imra_setup.iss is in the specified folder.
Intermapper will launch as soon as it is installed.
For subsequent installations
Run the following command:
@set NOLAUNCHIM=1
InterMapper_RemoteAccess_Setup_664.exe /s /a /SMS /f1"c:\temp\imra_setup.iss"Uninstalling Remote Access
To uninstall Intermapper RemoteAccess from a macOS system:
- Open the Applications folder.
- Drag the Intermapper RemoteAccess icon to the trash.
- Manually remove files that have com.dartware.*.plist or com.helpsystems.*.plist in the file names from the ../Library/Preferences folder.
Delete the Intermapper_Remote Access_6.6.4 directory and the Intermapper RemoteAccess icon from your desktop.
To uninstall Intermapper RemoteAccess from a Microsoft Windows system:
- Open the Control Panel.
- From Programs and Features, click Intermapper RemoteAccess.
- Click Uninstall and follow the prompts.