Fuzz Testing with the OSPFv3 Protocol
Overview
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 for IPv6 (OSPFv3), also known as OSPF for IPv6, is a Gateway Protocol (IGP), meaning it operates within a single autonomous system. Its purpose is to facilitate the exchange of routing information between routers, dynamically update the routing tables based on network topology changes and calculate the shortest path to each node.
Testing environment requirements
-
beSTORM 13.2.0 or later (licensed)
-
Windows 10 or later
-
A router that supports the OSPFv3 protocol (this will be the device under test [DUT])
Fuzzing with beSTORM
To fuzz with the OSPFv3 protocol in beSTORM, do the following:
-
Using a network cable, connect the OSPFv3-supported router (DUT) to the beSTORM computer's Ethernet adapter.
-
Open beSTORM Client.
-
Select New Project. The beSTORM New Project Wizard opens.
-
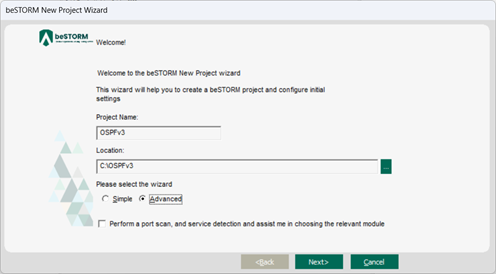
On the Welcome page, do the following:
-
In the Project Name box, enter a name.
-
Optionally, select a different file location for your project in the Location Name box.
-
For Please select the wizard, select Advanced.
-
Leave Perform a port scan, and service detection and assist me in choosing the relevant module unchecked.
-
-
Select Next.
-
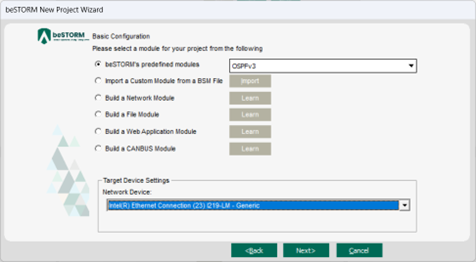
On the Basic Configuration page, do the following:
-
In the beSTORM's predefined modules list, select OSPFv3.
-
In the Network Device list, select the beSTORM computer's Ethernet adapter where you connected your network cable.
-
-
Select Next.
-
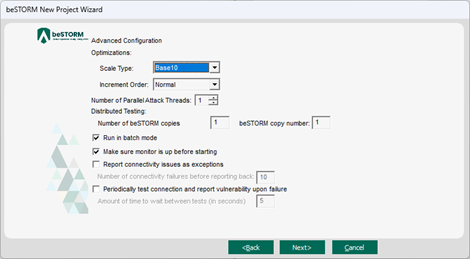
On the Advanced Configuration page, adjust Scale Type to reduce the number of combinations and overall testing duration. For the least number of combinations and shortest testing duration, select Base10.
-
Select Next.
-
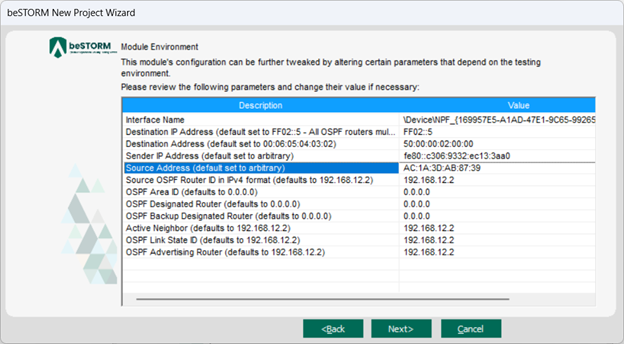
On the Module Environment page, do the following for the first five parameters:
-
Interface Name - In the Value box, confirm it is set to the Ethernet adapter you selected in step 6b.
-
Destination IP Address - In the Value box, enter the IP address of the DUT router (for the interface connected to in the router), or use the default FF02::5 value (this value in the OSPF protocol context is a multicast address where all routers running an OSPF protocol listen for packets).
-
Destination Address - Double-click the Value box. In the MAC Address Finder dialog, enter the IPv4 address of the DUT router (you cannot use the same multicast address used for the Destination IP Address parameter), and then select Find. The MAC Address box will refresh and display the MAC address of the IPsec computer. Select OK.
-
Sender IP Address - In the Value box, enter the IPv6 address of the beSTORM computer.
-
Source Address - Double-click the Value box. In the MAC Address Finder dialog, enter the IPv4 address of the beSTORM computer and then select Find. The MAC Address box will refresh and display the MAC address of the beSTORM computer. Select OK.
-
Optionally, you can adjust the remaining parameters to further refine OSPFv3 fuzzing with beSTORM.
-
-
Select Next.
-
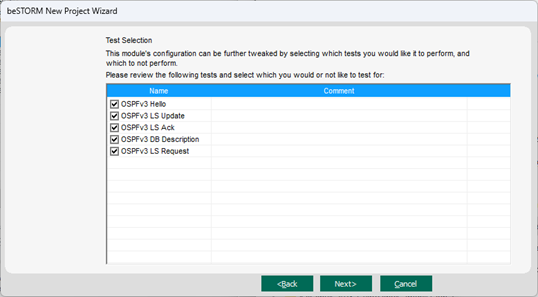
On the Test Selection page, select the OSPFv3 request types you want to fuzz.
-
Select Next.
-
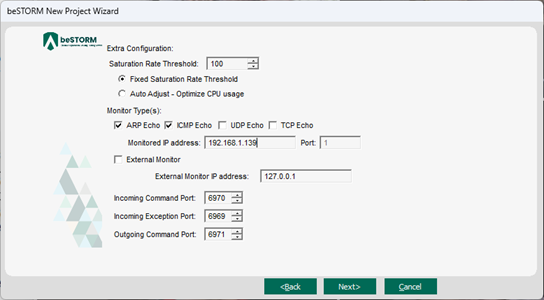
On the Extra Configuration page, do the following:
-
Select the ARP Echo and ICMP Echo checkboxes.
-
Set the Monitored IP Address to the router's IPv4 Address. Leave all other parameters to their default setting.
-
-
Select Next.
-
On the Complete beSTORM wizard page, select Finish to begin fuzzing, or clear the Auto-start beSTORM scan now checkbox to run the test later.
-
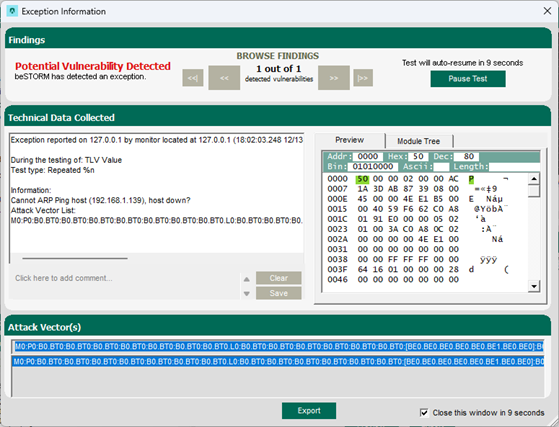
Once your test begins, if an exception occurs (that is, an attack was successful), a message will appear in an Exception Information dialog informing you that the router is not responding. This indicates a possible vulnerability. Testing will resume after five seconds unless you select Pause Test.
-
When fuzzing is complete, select Report > Generate Report from the beSTORM Client to generate a more comprehensive report of your Configuration page.