Fuzz Testing with the PTPv2 Server Protocol
Overview
The Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is a synchronization protocol for networked measurement and control systems. This topic describes how to test the Precision Time Protocol v2 (IEEE1588-2008) specifically as a primary (client) implementation beSTORM will act as a subordinate (server) with this protocol.
Testing environment requirements
-
beSTORM 13.3.0 or later (licensed)
-
Windows 10 or later
-
A device that supports the PTPv2 protocol, specifically as a primary implementation (this will be the device under test [DUT])
Fuzz testing with beSTORM
To fuzz with the PTPv2 (IEEEE 1588-2008) Server protocol in beSTORM, do the following:
-
Using a network cable, connect the PTPv2-supported device (DUT) to the beSTORM computer's Ethernet adapter.
-
Open beSTORM Client.
-
Select New Project. The beSTORM New Project Wizard opens.
-
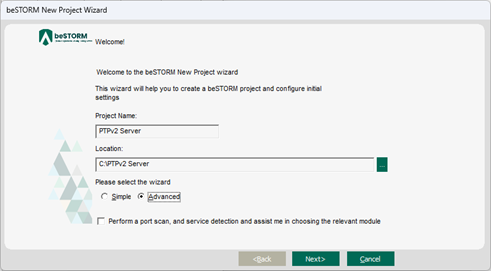
On the Welcome page, do the following:
-
In the Project Name box, enter a name.
-
Optionally, select a different file location for your project in the Location Name box.
-
For Please select the wizard, select Advanced.
-
Leave Perform a port scan, and service detection and assist me in choosing the relevant module unchecked.
-
-
Select Next.
-
On the Basic Configuration page, do the following:
-
In thebeSTORM's predefined modules list, select PTPv2 (IEEE1588-2008) Server.
-
Leave Protocol set to udp.
-
In the Local Port box, enter the port value of where beSTORM, acting as a subordinate, will listen for DUT requests. In most cases, leave this set to 319 (default).
NOTE: The DUT acting as a primary must send PTP requests to this port number.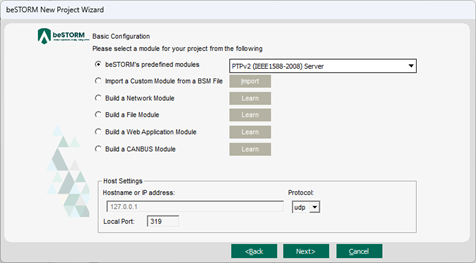
-
-
Select Next.
-
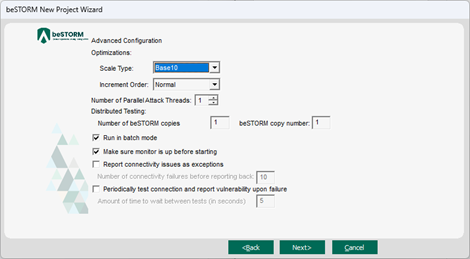
On the Advanced Configuration page, adjust Scale Type to reduce the number of combinations and overall testing duration. For the least number of combinations and shortest testing duration, select Base10.
-
Select Next.
-
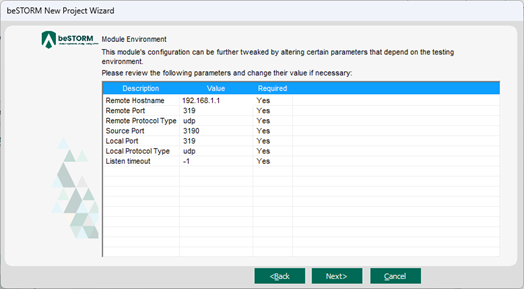
On the Module Environment page, verify the following default values appear in the corresponding Value box for each parameter:
-
Remote Hostname - DUT's IP address
-
Remote Port - 319
-
Remote Protocol Type - udp
- Source Port - 3190
-
Local Port - The local port where beSTORM will listen for DUT requests. Leave this set to its default value.
NOTE: beSTORM will act as a server in this module and will listen for incoming requests before sending fuzzing data (more details in step 14). - Local Protocol Type - udp
-
Listen timeout - Specifies the number of seconds that beSTORM will listen for DUT requests before timing out. The default is -1, which means beSTORM will wait indefinitely.
-
-
Select Next.
-
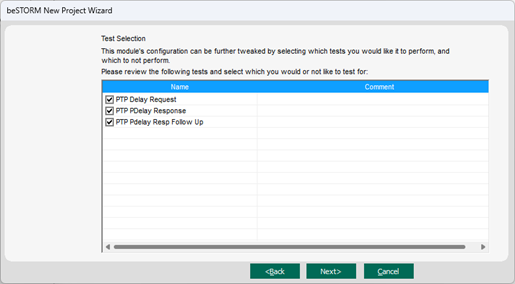
On the Test Selection page, select the PTPv2 request types you want to fuzz:
-
Delay Request is sent directly to the previously configured Remote Hostname IP address.
-
Peer Delay Response and Peer Delay Response Follow Up are the server's response to the DUT PTP client messages (that is, why the DUT must act as an active PTP primary (client).
-
-
Select Next.
-
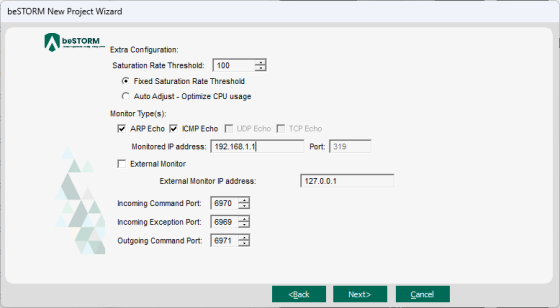
On the Extra Configuration page, do the following:
-
Select the ARP Echo and ICMP Echo checkboxes.
- Set the Monitored IP Address to the DUT's IP address.
-
If you can run software on the DUT, the beSTORM monitor for Windows (installed separately), or GDB monitor for Linux/Unix systems (sample gdb_monitor scripts are included), are ideal methods to monitor for failure with beSTORM using the External Monitor parameter.
-
Leave all other parameters to their default setting.
-
-
Select Next.
-
On the Complete beSTORM wizard page, select Finish to begin fuzzing, or clear the Auto-start beSTORM scan now checkbox to run the test later.
-
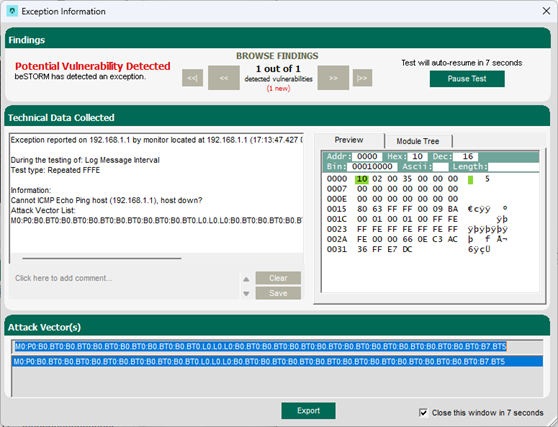
Once your test begins, if an exception occurs (that is, an attack was successful), a message will appear in an Exception Information dialog informing you that the router is not responding. This indicates a possible vulnerability. Testing will resume after five seconds unless you select Pause Test.
-
When fuzzing is complete, select Report > Generate Report from the beSTORM Client to generate a more comprehensive report of your Configuration page.