PE and Memory Indicators
The stage block in Malleable C2 profiles controls how Beacon is loaded into memory and edit the content of the Beacon DLL.
stage {
set userwx "false";
set compile_time "14 Jul 2009 8:14:00";
set image_size_x86 "512000";
set image_size_x64 "512000";
set obfuscate "true";
set rdll_loader "PrependLoader";
set eaf_bypass "true"; # EAF Bypass is only enabled for PrependLoader
transform-x86 {
prepend "\x90\x90";
strrep "ReflectiveLoader" "DoLegitStuff";
}
transform-x64 {
# transform the x64 rDLL stage
}
stringw "I am not Beacon";
transform-obfuscate {
lznt1;
rc4 "64";
xor "32";
base64;
}
}
The stage block accepts commands that add strings to the .rdata section of the Beacon DLL. The string command adds a zero-terminated string. The stringw command adds a wide (UTF-16LE encoded) string. The data command adds your string as-is.
The eaf_bypass option enables the PrependLoader to leverage gadgets inside of Windows system DLLs to bypass checks triggered by some security solutions when reading Export Address Table (EAT) information during the loader's function address resolution steps. The eaf_bypass option in 32-bit Beacons performs additional checks before searching for gadgets for maximum compatibility. If EAF enforcment is not detected, the eaf_bypass option is silently disabled, which mitigates crashes on older Windows systems and only affects the eaf_bypass option in 32-bit Beacons.
The transform-x86 and transform-x64 blocks pad and transform Beacon’s Reflective DLL stage. These blocks support three commands: prepend, append, and strrep.
The prepend command inserts a string before Beacon’s Reflective DLL. The append command adds a string after the Beacon Reflective DLL. Make sure that prepended data is valid code for the stage’s architecture (x86, x64). The c2lint program does not have a check for this. The strrep command replaces a string within Beacon’s Reflective DLL.
The transform-obfuscate block performs additional transformations to the Beacon’s DLL payload. This block is only supported when the stage.rdll_loader is set to PrependLoader. The following transformations are supported: base64, lznt1, rc4, and xor. The transformations are applied in the order they appear in the transform-obfuscate block, and you can apply as many as you require. The CobaltStrike PrependLoader will process the transformations in reverse order to get to the original Beacon DLL payload to load it into memory. A xor transformation with a key length of 32 is applied by default.
The base64 transformation encodes the Beacon’s DLL payload using base64 encoding. This transformation command optionally supports a key length but only applies additional random data to the payload.
The lznt1 transformation compresses the Beacon’s DLL payload using a LZNT1 compression. This transformation command optionally supports a key length but only applies additional random data to the payload.
The rc4 transformation encrypts the Beacon’s DLL payload using RC4 encryption. This transformation command requires a key length to generate a random key to use for the encryption algorithm.
The xor transformation encrypts the Beacon’s DLL payload using xor encryption. This transformation command requires a key length to generate a random key to use for the encryption algorithm.
The key length's character range size for the base64 transformation, lznt1 transformation, and xor transformation is 8-2048 characters. Any length outside this range will default to 32 characters.
The key length for the rc4 transformation is limited to 128 characters. Exceeding this limit will fail to obfuscate the payload.
The transform-obfuscate setting is independent of other transformation settings; however, when it is set or defined, the transformations are applied to the Beacon’s DLL payload in this order:
-
stage.obfuscate
-
stage.transform-[x86|x64].strrep commands
-
stage.transform-obfuscate transformation commands
-
stage.transform-[x86|x64] all commands
The stage block accepts several options that control the Beacon DLL content and provide hints to change the behavior of Beacon’s Reflective Loader:
| Option | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| allocator | HeapAlloc | Set how Beacon's Reflective Loader allocates memory for the agent. Options are: HeapAlloc, MapViewOfFile, and VirtualAlloc. |
| cleanup | true | Ask Beacon to attempt to free memory associated with the Reflective DLL package that initialized it. |
| copy_pe_header | true | Ask the Reflective Loader to copy Beacon to new memory location with its DLL headers. |
| data_store_size | 16 | Set how many entries can be stored in Beacon Data Store. |
| eaf_bypass | true | The eaf_bypass option enables the PrependLoader to leverage gadgets inside of Windows system DLLs to bypass checks triggered by some security solutions when reading Export Address Table (EAT) information during the loader's function address resolution steps. |
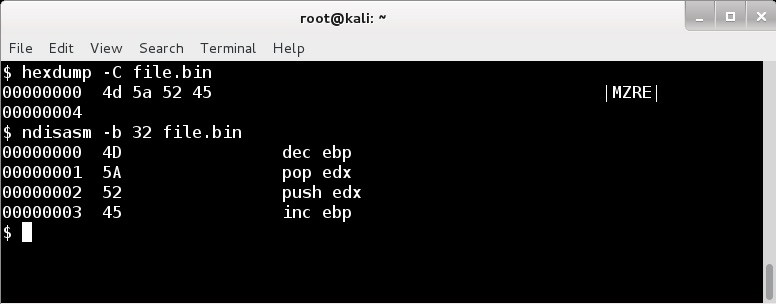
| magic_mz_x862 | MZRE | Override the first bytes (MZ header included) of Beacon's Reflective DLL. Valid x86 instructions are required. Follow instructions that change CPU state with instructions that undo the change. |
| magic_mz_x642 | MZAR | Same as magic_mz_x86; affects x64 DLL |
| magic_pe | PE | Override the PE character marker used by Beacon's Reflective Loader with another value. |
| module_x861 | xpsservices.dll | Ask the x86 ReflectiveLoader to load the specified library and overwrite its space instead of allocating memory with VirtualAlloc. |
| module_x641 | xpsservices.dll | Same as module_x86; affects x64 loader |
| obfuscate | false | Obfuscate the Reflective DLL’s import table, .TEXT section, and overwrite unused header content. |
| rdll_loader | Prependloader | Set which Reflective Loader to use when generating Beacon payloads. Options are: PrependLoader and StompLoader. |
| rdll_use_syscalls | true | Ask the Reflective Loader to use indirect system calls when loading the Beacon payload. The option is only valid when the rdll_loader is set to PrependLoader and the allocator is set to VirtualAlloc or MapViewOfFile. In other cases, the standard Kernel32 APIs will be used. |
| sleep_mask | true | Obfuscate Beacon, its heap allocations, and the Sleepmask (in-memory) prior to sleeping. |
| smartinject | false | Use embedded function pointer hints to bootstrap Beacon agent without walking kernel32 EAT. The option is only valid when the rdll_loader is set to StompLoader. |
| stomppe | true | Ask ReflectiveLoader to stomp MZ, PE, and e_lfanew values after it loads Beacon payload |
| syscall_method | None | Set the system call method to use on initial beacon execution. Options are None, Direct, Indirect. See section System Calls for additional information. |
| userwx | false |
Ask ReflectiveLoader to use or avoid RWX permissions for Beacon DLL in memory |
1. - The module_x86 and module_x64 setting now supports the ability to specify the starting ordinal value to search for an exported function. The optional 0x## part is the starting ordinal value specified as an integer. If a library is set and Beacon does not overwrite itself into the memory space then it likely the library does not have an exported function with an ordinal value of 1 through 15. To resolve this determine a valid ordinal value and specify this value using the optional syntax, for example: set module_x64 "libtemp.dll+0x90"
2. - When using the PrependLoader, the magic_mz_86 and magic_mz_x64 settings do not need to be valid x86 instructions as these bytes are not executed. The value can not exceed 59 characters.
Cloning PE Headers
The stage block has several options that change the characteristics of your Beacon Reflective DLL to look like something else in memory. These are meant to create indicators that support analysis exercises and threat emulation scenarios.
| Option | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| checksum | 0 | The CheckSum value in Beacon’s PE header |
| compile_time | 14 July 2009 8:14:00 | The build time in Beacon’s PE header |
| entry_point | 92145 | The EntryPoint value in Beacon’s PE header |
| image_size_x64 | 512000 | SizeOfImage value in x64 Beacon’s PE header |
| image_size_x86 | 512000 | SizeOfImage value in x86 Beacon’s PE header |
| name | beacon.x64.dll | The Exported name of the Beacon DLL |
| rich_header | Meta-information inserted by the compiler |
Cobalt Strike’s Linux package includes a tool, peclone, to extract headers from a DLL and present them as a ready-to-use stage block:
./peclone [/path/to/sample.dll]
Reflective Loader Drip-Loading
The Cobalt Strike Reflective Loader supports the option to drip-load Beacon into memory. Drip-loading is a technique that attempts to avoid making large allocations of memory, which could be used as a heuristic for code injection. Instead, memory is allocated numerous times using the smallest size chunks supported by the OS. Drip-loading is performed by:
-
Reserving the target memory and committing it.
-
Writing the payload over in chunks.
-
Modifying the page protection on individual chunks.
Furthermore, delays are also introduced to attempt to avoid event correlation typically associated with code injection (i.e., allocating a block of memory, writing a payload, and then starting a new thread all in quick succession).
While this feature is disabled by default, users can enable it by setting the following malleable C2 profile settings in the stage block:
set rdll_use_driploading "true";
set rdll_dripload_delay "100";
To control the delay of the sequence of events, set the rdll_dripload_delay in milliseconds (default is 100ms). Do not increase the value too significantly beyond a few hundred milliseconds, as this will drastically slow down the time it takes for the Reflective Loader to get Beacon into memory and running. It is highly advised to test different delays to determine what you are comfortable using.
In-memory Evasion and Obfuscation
Use the stage block’s prepend command to defeat analysis that scans the first few bytes of a memory segment to look for signs of an injected DLL. If tool-specific strings are used to detect your agents, change them with the strrep command.
If strrep isn’t enough, set sleep_mask to true. This directs Beacon to obfuscate itself and it's heap in-memory before it goes to sleep. After sleeping, Beacon will de-obfuscate itself to request and process tasks. The SMB and TCP Beacons will obfuscate themselves while waiting for a new connection or waiting for data from their parent session.
Decide how much you want to look like a DLL in memory. If you want to allow easy detection, set stomppe to false. If you would like to lightly obfuscate your Beacon DLL in memory, set stomppe to true. If you’d like to up the challenge, set obfuscate to true. This option will take many steps to obfuscate your Beacon stage and the final state of the DLL in memory. In addition, when using the Prepend Reflective Loader, use the transform-obfuscate settings to add additional obfuscations to your Beacon stage. If you do not want the Beacon DLL’s headers copied to the final memory location, set copy_pe_header to false.
When using the Prepend Reflective Loader, the reflective loading process does not use the MZ and PE magic bytes. You can set these bytes to any value as long as you do not exceed the character length limits. The magic_pe is limited to 2 characters, and magic_mz_x86 and magic_mz_x64 are limited to 59 characters.
When using the Stomp Reflective Loader, one way to find injected DLLs is to look for the MZ and PE magic bytes at their expected locations relative to each other. These values are not usually obfuscated as the reflective loading process depends on them. The obfuscate option does not affect these values. Set magic_pe to two letters or bytes that mark the beginning of the PE header. Set magic_mz_x86 to change these magic bytes in the x86 Beacon DLL. Set magic_mz_x64 for the x64 Beacon DLL. Follow instructions that change CPU state with instructions that undo the change. For example, MZ is the easily recognizable header sequence, but it's also valid x86 and x64 instructions. The follow-on RE (x86) and AR (x64) are valid x86 and x64 instructions that undo the MZ changes. These hints will change the magic values in Beacon's Reflective DLL package and make the reflective loading process use the new values.
figure 69 - Disassembly of default module_mz_x86 value
Set userwx to false to ask Beacon’s loader to avoid RWX permissions. Memory segments with these permissions will attract extra attention from analysts and security products.
By default, Beacon’s loader allocates memory with VirtualAlloc. Use the allocator option to change this. The HeapAlloc option allocates heap memory for Beacon with RWX permissions. The MapViewOfFile allocator allocates memory for Beacon by creating an anonymous memory mapped file region in the current process. Module stomping is an alternative to these options and a way to have Beacon execute from coveted image memory. Set module_x86 to a DLL that is about twice as large as the Beacon payload itself. Beacon’s x86 loader will load the specified DLL, find its location in memory, and overwrite it. This is a way to situate Beacon in memory that Windows associates with a file on disk. It’s important that the DLL you choose is not needed by the applications you intend to reside in. The module_x64 option is the same story, but it affects the x64 Beacon.
If you’re worried about the Beacon stage that initializes the Beacon DLL in memory, set cleanup to true. This option will free the memory associated with the Beacon stage when it’s no longer needed.