![]()
EFT Server adheres to the OpenPGP standard and is RFC 2440 compliant. OpenPGP is a standard and has no version. Refer to RFC 2440 for details.
EFT Server employs industry-standard OpenPGP (based on the open source implementation of Pretty Good Privacy) technology to safeguard data at rest. In contrast to symmetric encryption technologies that rely on a single password or shared secret for encryption and decryption, OpenPGP uses a public/private key pair and a password. Although widespread, dual-factor encryption technologies such as PGP are not universally employed throughout the industry, because of the complexities involved in key creation, management, and distribution, as well as the application of public-key infrastructure technologies. Another drawback is the fact that the entire file must be present for PGP encryption to work, resulting in a very brief period of time whereby data is stored "in the clear," until the encryption process is completed and the source (unprotected) file is deleted.
|
|
EFT Server adheres to the OpenPGP standard and is RFC 2440 compliant. OpenPGP is a standard and has no version. Refer to RFC 2440 for details. |
How PGP Encrypt/Decrypt Works
Below are illustrations of how PGP encryption and decryption works.
Encryption:
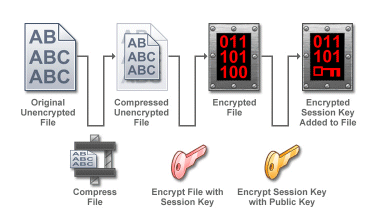
Decryption:
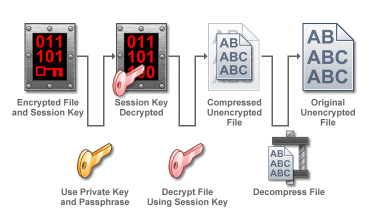
In EFT Server, the OpenPGP data encryption (or decryption) process is directed by Event Rules that specify how data files are treated in a particular context. OpenPGP uses a public key (a message encrypted with a recipient's public key cannot be decrypted by anyone except the recipient possessing the corresponding private key. See Private Key) and a private key (the server's private key decrypts the client's session. The private key has a .key extension and is part of the public-private key pair) to encrypt data and maintain security. These two components are considered a key pair and are associated with a particular Site (In EFT Administrator, a Site is similar to a virtual FTP server bound to one or more IP addresses.). The key pair is stored on the OpenPGP Key Ring, which is the management tool for public keys and key pairs. The OpenPGP Key Ring contains all key information and allows import, export, creation, and deletion of keys.
New key pairs are created using the OpenPGP Key Generation wizard. The wizard prompts you for key parameters and creation of a passphrase. Once the new key pair is generated, you must determine if the new key pair will be the default for the entire Site. Allowing assignment of a default key pair will automatically select this key when configuring an Event Rule using OpenPGP encryption.
The example below shows how a trigger event (On Upload) is used to initiate OpenPGP encryption.
In an Event Rule, when a selected even occurs (e.g., a file is uploaded to the server), if the specified Condition exists (e.g., user is member of group A), then the selected actions occur (e.g., encrypt the file).
OpenPGP encryption is only available for certain events:
On Upload - when a file is uploaded to a location.
On Rotate Log - when a log file is closed out and a new log initiated.
On Timer - an event that occurs once or according to a schedule.
Below is a simplified example of the file transfer process in which EFT Server uses OpenPGP to encrypt uploaded data and the off-load capabilities of EFT Server to move the file to another location.
Creating Key Pairs for OpenPGP
Deleting Key Pairs for OpenPGP