You can use the AS2 Send file to host Action to configure Event Rules to cause AS2 traffic to route through the DMZ Gateway. You can use the AS2 Send File to host Action in the Folder Monitor, Timer, and all file-based Events.
To route AS2 traffic through DMZ Gateway
Create a new Event Rule, such as a File Uploaded event. (Refer to Creating Event Rules for details of creating Event Rules, if necessary.)
Add the AS2 Send file to host Action to the Rule, then click the file or host link. The AS2 Send File dialog box appears.
Define the trading partner options (in the AS2 Send File dialog box).
Add the Copy/Move File to Host Action to the Rule.
In the Rule Builder
pane, click any one of the undefined parameters (e.g., %FS.PATH%).

The Offload Action wizard appears.
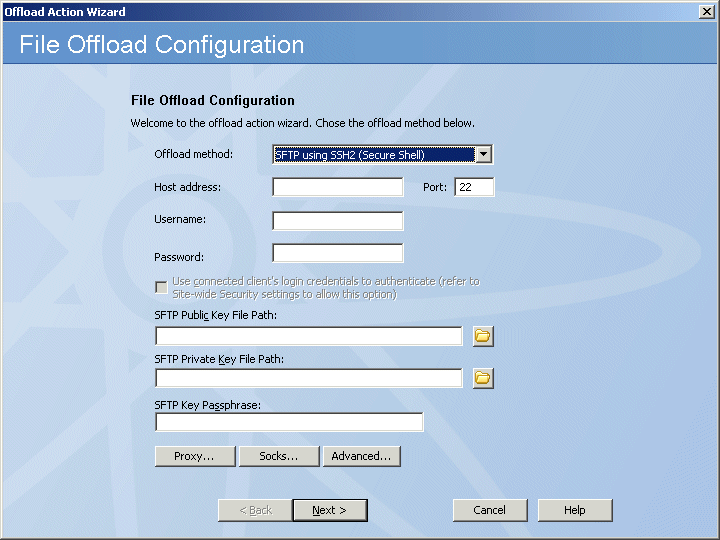
On the Offload method box, specify a protocol type for the connection: Local (Local File or LAN), FTP (standard File Transfer Protocol), FTP SSL/TLS (AUTH TLS), FTP with SSL (Explicit encryption), FTP with SSL (Implicit encryption), SFTP using SSH2 (Secure Shell), HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol), HTTPS (Secure HTTP access).
In the Host address box, type the IP address.
The Port number for the selected protocol changes automatically based on the offload method. Provide a different port number, if necessary.
Provide the Username and Password needed to establish the connection.
Select the Use connected client's login credentials to authenticate check box if you want to use the local system account to authenticate.
If you chose SFTP:
In the SFTP Public Key File Path box, type the path or click the folder icon to browse to and select the path.
In the SFTP Private Key File Path box, type the path or click the folder icon to browse to and select the path.
In the SFTP Key Passphrase box, provide the key's passphrase.
Click Proxy.
The Proxy Settings dialog
box appears.
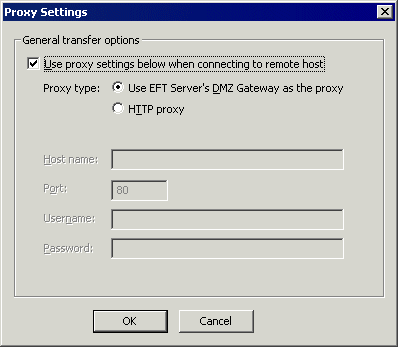
Specify the Proxy type, Host name, Port, Username, and Password.
|
|
Using the DMZ Gateway as proxy is available only in the Enterprise edition of EFT Server. |
To specify an Authentication Type and login sequence, configure the Advanced settings.
Specify one of the following Authentication Types:
USER user @site if your proxy server requires the USER command followed by your user name and the Site name to allow connection with a remote Site. You can change the @ symbol if a different separator is required by your proxy server.
SITE site if your proxy server requires the SITE command followed by the address of the remote FTP site to allow a connection.
USER with logon if your proxy server requires the USER command followed by a user name and password to allow connection with a remote Site.
USER/PASS/ACCT if your proxy server requires all three commands before allowing a connection to a remote Site.
OPEN site if your proxy server requires the OPEN command followed by the Site name before allowing connection to the Site.
Custom if your proxy server requires a login sequence different from those above. Refer to To create a custom authentication method for a proxy server below for details of creating a login sequence.
To specify transfer options and time stamps, click Advanced. The Advanced Options dialog box appears.
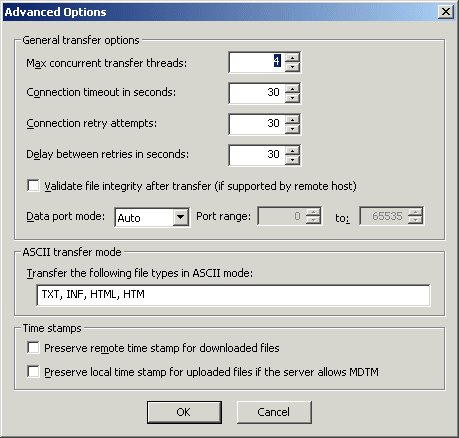
In the General transfer options area, you can provide more control over Max concurrent transfer threads, Connection timeout, Connection retry attempts, and Delay between retries. When files are being transferred with Event Rules (copy/move), if there are connection problems (e.g., the network is unavailable), EFT Server will attempt to establish a connection the number of times specified in Connection retry attempts. When EFT Server is able to re-establish the connection, it continues to transfer the file even if there are multiple interruptions.
Select the Validate file integrity after transfer check box to specify that EFT Server should double check binary files to ensure the files downloaded completely and correctly.
In the Data port mode box, click the drop-down list and select one of the following:
Auto - (selected by default) EFT Server initially makes connections in PASV mode. If the PASV connection fails, EFT Server attempts to connect in PORT mode automatically.
PASV - Helps avoid conflicts with security systems. PASV support is necessary for some firewalls and routers, because with PASV, the client opens the connection to an IP Address and port that EFT Server supplies.
PORT - Use PORT when connections or transfer attempts fail in PASV mode, or when you receive data socket errors. When a client connects using PORT, EFT Server opens a connection to an IP address and port that the client supplies. If you select Port, specify the Port range.
In the ASCII transfer mode area, specify the file types that can be transferred. TXT, INF, HTML, and HTM are specified by default.
In the Time stamps area, select one of the following:
Select the Preserve remote time stamp for downloaded files check box to keep a downloaded file's time stamp the same on the local computer as it is on EFT Server.
Select the Preserve the local time stamp for uploaded files if EFT Server allows MDTM check box to keep an uploaded file's time stamp the same on EFT Server as it is on the local computer.
Click OK.
Click Next. The Source File Path page appears.
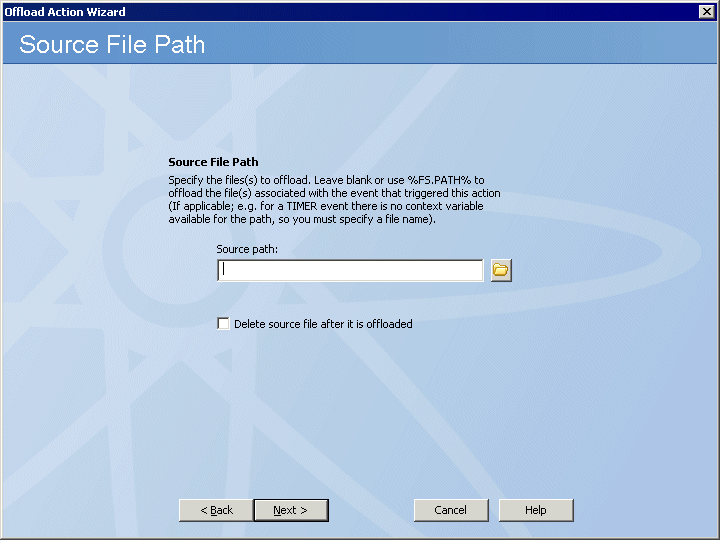
In the Source path
box, provide the path to the file(s) that you want to offload. For example,
type:
/pub/usr/jsmith/file.txt or \\mydomain\common\jsmith\file.txt
If you want to Delete source file after it has been offloaded, select the check box.
Click Next. The Destination File Path page appears.
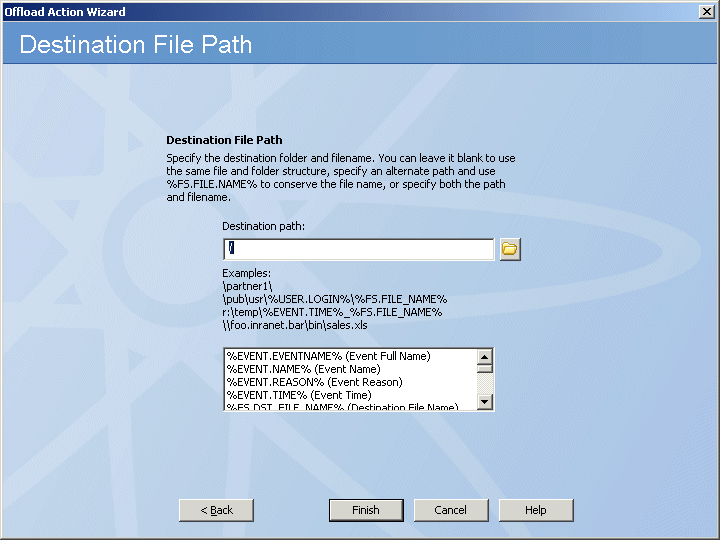
In the Destination
path box, click the folder icon ![]() and specify the location in which to save the
offloaded file.
and specify the location in which to save the
offloaded file.
You can also specify variables, such as \pub\usr\%USER.LOGIN%\%FS.FILE.NAME%. In the Variables box, double-click the variable(s) that you want to add to the path.
Click Finish then click Apply to save the changes on EFT Server and/or add other Actions and Conditions to the Rule.
If you are copying or moving the file to another location, and the file upload is a regularly occurring event with a file of the same name, in the Offload Action wizard, add the variables %EVENT.DATESTAMP% and/or %EVENT.TIMESTAMP% to the path so that the date (YYYYMMDD) and/or time (HHMMSS) are added to the filename when it is moved/copied. Do not use %EVENT.TIME%, because the colon (e.g., 28 Aug 07 10:01:56) makes it unsuitable for file naming.
For example, in the Offload Action wizard, in the Destination path box, provide the path and variables. For example, type:
C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\My Documents\upload/%EVENT.DATESTAMP%_%EVENT.TIMESTAMP%_%FS.FILE_NAME%
With this path and variables, when a file is uploaded to the monitored folder, the file is moved to \My Documents\upload and the date and time are prepended to the filename. For example, 20080422_101212_mydailyprogress.doc.
To create a custom authentication method for a proxy server
|
|
Contact your system administrator for the proper Host name, Port, User name, Password, and proxy type, as well as any required advanced authentication methods. |
In the Proxy Settings dialog box (see step 12 above), click Advanced. The Advanced Proxy Settings dialog box appears.
In the Advanced Proxy Settings dialog box, click Custom, then specify the login sequence in the text box using the following variables:
%host% - sends the host name you typed in the Proxy server options dialog box.
%user% - sends the user name you typed in the Proxy server options dialog box.
%pass% - sends the password you typed in the Proxy server options dialog box.
%port% - sends the port number you typed in the Proxy server options dialog box.
%fire_pass% - sends the password you typed in the Proxy server options dialog box as authentication for the firewall.
%fire_user% - sends the user name you typed in Proxy server options dialog box as authentication for firewall.
Type each variable with percent signs before and after.
Press ENTER to separate commands.
Type any other commands and variables, separating commands with a line break (press ENTER).
Click OK.
Click Apply to save the Rule.