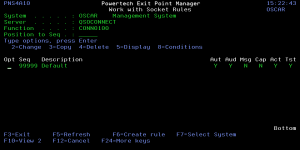
How to Get There
On the Exit Point Manager Main Menu, choose option 20, then choose option 2.
What it Does
The Work with Socket Rules panel allows you to view or change Socket Rules.
Socket Rules are examined by Powertech Exit Point Manager exit programs until a match is found (based on a Socket Rule's Socket Conditions).
Field Descriptions
System
System indicates the target of any operations you perform. When you add rules, for example, those rules will be sent to, and will affect processing on, the System named.
Server
A Server in Exit Point Manager is a controlled entry point into your system. These entry points are determined and defined by IBM. Exit Point Manager has assigned easy-to-remember names to these controlled entry points.
Function
A Function, or Server Function, in Exit Point Manager represents a class of operations that a given Server may perform. For example, the *SIGNON Server classifies its operations as those pertaining to changing passwords, generating authentication tokens, and retrieving signon information. Exit Point Manager has assigned easy-to-remember names to these Functions, such as CHGPWD, GENAUTTKN and RETRIEVE.
Position to seq
Used to position the list.
Seq
The sequence number of a Socket Rule determines the order in which it will be evaluated by the exit program, with the lowest sequence number being evaluated first. Socket Rules are evaluated until a match is found.
Description
The Socket Rule description is a short textual description of the Socket Rule. It is typically used to indicate the purpose of the Socket Rule.
Aut
Authority represents the action to be taken when a rule is found that matches the data present on a transaction.
The valid values are:
The value * will cause the rule to inherit the value from the default Socket Rule (sequence number 99999). This default rule may not be set to the value *.
Aud
The Audit transactions flag controls the logging of transactions to the Log Journal set up on the Work with Exit Point Manager System Values panel.
The valid values are:
The value * will cause the rule to inherit the value from the default Socket Rule (sequence number 99999). This default rule may not be set to the value *.
Msg
The Send messages flag controls the sending of messages to the Log Message Queue set up on the Work with Exit Point Manager System Values panel.
The value * will cause the rule to inherit the value from the default Socket Rule (sequence number 99999). This default rule may not be set to the value *.
Cap
The Capture transactions flag controls whether transactions are remembered in Exit Point Manager. Unlike some other rule types, a captured Socket Rule cannot be memorized.
The valid values are:
The value * will cause the rule to inherit the value from the default Socket Rule (sequence number 99999). This default rule may not be set to the value *.
Act
The Socket Rule Active flag determines whether the rule will be evaluated by the exit point program.
It can be useful to initially set a Socket Rule as not active in order to test it without enforcing it.
The valid values are:
The value N is not allowed for the default Socket Rule (sequence number 99999).
Tst
The Socket Rule Test flag determines whether the rule will be evaluated by the Socket Rule test facility.
It can be useful to flag a rule to not be tested in order to verify the effects of removing that rule.
The valid values are:
The value N is not allowed for the default Socket Rule (sequence number 99999).
Opt
Enter a valid option from the list of options provided on the list panel.
Options
2=Change
Choose this option to open the Change Socket Rule panel, where you can modify a Socket Rule's attributes.
3=Copy
Choose this option to open the Copy Socket Rule panel, where you can copy a Socket Rule.
4=Delete
Choose this option to delete the Socket Rule.
5=Display
Choose this option to display the Socket Rule.
8=Conditions
Choose this option to open the Work with Socket Conditions panel, where you can view or change Socket Conditions.
Command Keys
F3 (Exit): Exit the current panel without processing any pending changes.
F5 (Refresh): Refreshes the panel with the most current data.
F6 (Create): Creates a new item.
F7 (Select System): Use this command key to work with data from a different System.
F12 (Cancel): Discards changes and returns to the prior panel.
F13 (Display msgs): Displays messages for the current user.
F14 (Work sbm job): Displays jobs submitted from the current user.
F15 (Work w/spooled files): Works with spooled files for the current user.
F24 (More keys): This shows additional function keys that can be used for this display.