Monitoring NT Services with the Microsoft Windows NT Services Probe
Intermapper can monitor and send notifications for NT Services running on another system. Intermapper uses the Service Control Manager facilities of the underlying Microsoft Windows host to communicate with a remote computer to track the state of its services.
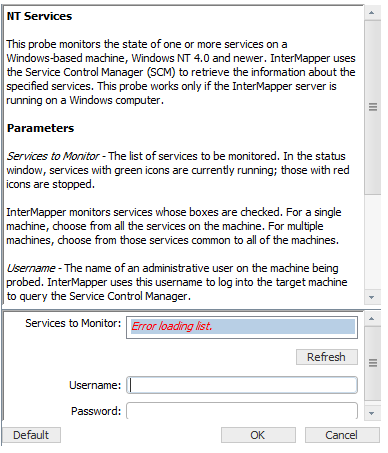
NT Services Preferences Panel
The NT Services configuration window displays the full list of services that are running on a remote host. You can select one or more services to monitor; Intermapper and receive an alert if any of them fails. The following are the probe parameters:
- A list of NT services on the target machine. This list displays red and green icons to indicate if the service is currently running. To receive an alert when a system fails, select the service.
- The Username and Password required to log into the target machine.
Authentication for NT Services Probe
The NT Services probe opens the Service Control Manager (SCM) on the target machine; hence, some authentication is required before this can happen. There are several ways to do this.
- Using built-in username and password:Intermapper has the built-in ability to solicit from you a username and
password for authentication. When you choose the NT Services probe, it
will prompt you for a username and password before attempting to connect
to the target machine. If you have not used one of the methods below,
fill in a username and password at that point and click OK. This will
be all you need to do for authentication; the username and password will
be saved.
NOTE: For this to work, Intermapper must be running as an administrator, as only administrators are empowered to make the required network connections. You can do this in one of two ways:
- The first way is by adjusting the account under which Intermapper is run. Intermapper is normally installed under the LocalSystem account, which does not have administrator privileges. To change the account under which it runs, go to the SCM and stop the Intermapper service if it is running. Right-click and select Properties. Select the Log On tab. Under Log On As, click the radio button next to This account and click Browse to list the accounts; choose an account with administrator privileges. Fill in the password for the account in Password and Confirm Password. Click OK.
The second way is to allow Intermapper to be an administrator when it needs to be by supplying it with an administrator's username and password, so that it can elevate its privileges when it needs to. You can do this using the NT Services item in the Server Settings list.
- The NET USE command. Another way
to authenticate is to use the NET USE command to create a connection between
the host machine and the target. For instance, to monitor the services
on a host at 192.168.1.140, enter the following:
NET USE \\192.168.1.140\ipc$ /USER:Administrator
You will be prompted for the password, and the connection will be made. (If you have done this, when prompted for a username and password for NT Services by Intermapper, you can leave them blank and click OK.)
NOTE: You must use the IP address and not the network name for the machine. That is important, as the Windows OS will not see the DNS name or the domain name as being the same as 192.168.1.140 when checking the connections, and will not recognize that there is a connection when Intermapper tries to query the services by IP address, returning an "access denied" error instead. - Synchronizing Users: A third way
to authenticate is to make sure that the user and password under which
the Intermapper service is running exists on the target machine as well.
When Intermapper is first installed, it is installed running under the user "LocalSystem", as most services are. It is necessary to create a new user on your machine; let's name it "Intermapper"> and give it a password. Make sure it is a member of Administrators. (If you already have a username and password that exist on all machines that are to be targeted by the NT Services probe as well as the Intermapper host and which has Administrator permissions everywhere, you can skip the previous step and substitute it for Intermapper in the following.)
Go to the SCM and stop the Intermapper service if it is running. Right-click and select Properties. Select the Log On tab. Under Log On As, click the radio button next to This account and click Browse to list the accounts. Select Intermapper. Fill in the password for the account in Password and Confirm Password. Click OK.
On the target machine, create a new user, also named Intermapper, with the same password and a member of Administrators.
Start Intermapper from the SCM on the original machine. You can now use NT Services probes. (When prompted for a username and password for NT Services by Intermapper, you can leave them blank and click OK.)
Error Messages
Intermapper may encounter authentication errors when attempting to connect. Here is a list of the messages and ways you might work around them:
- Error attempting to elevate privileges. Intermapper is not running as an administrator, and thus needs to elevate its privileges in order to be able to execute the NT Services probe. It could not do so. Make sure a correct username and password for the Intermapper host machine have been supplied in the NT Services panel of the Server Settings dialog. Make sure the user given has the right to log on as a service in your Local Security Policy. If host machine is Microsoft Windows Server 2003 or newer, make sure the user has the right to impersonate another user.
- Could not establish Microsoft Windows Networking connection to probe target. When a username and password have been supplied for the target machine, Intermapper attempts to use them to create a connection between the host and the probe target. This attempt failed for some reason. Will be followed by more specific error information. See below.
- Could not open SCM on probe target. Intermapper could not open the Service Control Manager on the target machine. Is followed by more specific error information. See below.
The following errors might be appended to the messages above:
- Access is denied. Make sure Intermapper is running as an administrator, or that an administrator username and password have been provided in the NT Services panel in the Server Settings dialog. Make sure a valid administrator username and password have been supplied for the probe target. If the probe target is running Microsoft Windows XP, make sure that "Simple Networking" is turned off.
- The network name cannot be found. and The network path was not found. The device you have specified does not appear to exist on the network. If you are sure that it does, make sure it is a Microsoft Windows machine with File and Print Sharing turned on, and that any firewall has exceptions for File and Print Sharing.
- An extended error has occurred. A network-specific error has occurred. It should be followed by more information about the nature of the error. You might need to consult your network administrator.
- The specified network password is incorrect. The password you supplied doesn't match the username.
- No network provider accepted the given network path. and The network is not present or not started. No network is present, or a component of the network is not started. Consult your network administrator.
- The RPC server is unavailable. Make sure that probe target is a Microsoft Windows machine with File and Print Sharing turned on, and that any firewall has exceptions for File and Print Sharing.