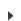Daemons
Security Auditor allows you to define your policy for daemons regardless of whether they should be required to be running, restricted from running, or whether it doesn’t matter whether they are running or not.
Initializing
Initializing this category will result in a list of the daemons currently on the server.
To initialize the Security Auditor Daemon category:
- Go to Servers > Initialize Policies.
- Select the server or servers you would like to initialize for Private policies. To initialize a shared policy, select a single server.
- Select the Policies tab.
- Choose whether this is a Private or Group policy.
- Choose the Daemon category.
- Click Initialize.
- Daemons currently running will be set to a policy value of Required.
- Daemons not running will be set to a policy value of Prohibited.
Using the Daemon category
Once initialized, you can alter the daemon settings to indicate whether they are Required (must be running), Prohibited (cannot be running) or Allowed (can be running or stopped.)
You can delete a daemon from the category. This does NOT delete the daemon from the server – only from the policy and subsequent compliance checks.
Running a compliance check
When a compliance check is run against the Daemon category, the values specified in the policy will be compared against the setting of the daemon on the server. The daemon will be in compliance if the server setting is the same as the Policy Value (or if the Policy Value is set to allowed). If the current setting is different than the value defined in the policy, the value will be flagged as “out of compliance.”
To run a compliance check, do one of the following:
- On the Manage Servers screen, click
 and choose whether you want to check the Private Policy, Group Policy, or both for the server (or Server Group).
and choose whether you want to check the Private Policy, Group Policy, or both for the server (or Server Group). - On the Manage Servers screen, click
 next to a server to open the server's Daemon policies.
next to a server to open the server's Daemon policies.- Click
 for the Daemon under the Action column. Or,
for the Daemon under the Action column. Or, - Select one or more Daemons and click CheckIt. This will run a compliance check on all the selected daemons in the Daemon category.
- Click
- Choose Servers > CheckIt. Choose the server from the Servers tab and then Daemons’ from the Policies tab, then click CheckIt.
- Schedule a regular compliance check. Go to Admin tasks > Manage Scheduled Jobs.
Discovering new daemons
As mentioned earlier, you can remove a daemon from the category. Deleting a daemon does not remove it from the server. If you wish to include the daemon again or discover other daemons that may be running on the server, do the following:
- Run a compliance check on the category and resolve any compliance issues (if any).
- Go to Servers > Initialize Policies and initialize the policy for the Daemon category. This will bring in the daemons currently on the partition, including any daemons previous deleted from the category.
Running FixIt
If an item is identified as Out of compliance ( ), you can have Security Auditor change the value to make it match the policy by running the Security Auditor FixIt function. By default, FixIt is not enabled. You must enable FixIt.
), you can have Security Auditor change the value to make it match the policy by running the Security Auditor FixIt function. By default, FixIt is not enabled. You must enable FixIt.
FixIt will start or stop the daemon based on the setting defined in the policy. FixIt will not take any action on daemons whose setting is Allowed.
Once a compliance check has been run and FixIt is enabled, do one of the following:
- Check the individual daemon or all daemons and then click FixIt.
- Choose Servers > FixIt. Choose the server and then the category, then click FixIt.
- Schedule a regular compliance check and FixIt. Choose Admin Tasks > Manage Scheduled Jobs.
- biod
- cron
- ctrmc
- IBM AuditRM
- IBM.CSMAgentRM
- IBM.DMSRM
- IBM.DRM
- IBM.ERRM
- IBM.HostRm
- IBM.HWCTRLRM
- IBM.LPRM
- IBM.SensorRM
- IBM.ServiceRM
- inetd
- nfsd
- portmap
- qdaemon
- rpc.lockd
- rpc.statd
- sshd
- syslogd
- xntpd
These daemons will also be noted in the Daemons category with an ‘*’. These items will be identified as out of compliance but FixIt will not modify their values.

 Previous
Previous