Starting and Stopping
the Server
The Server starts automatically and runs as a Windows system service.
If you close the Administrator, the Server continues to run in the background
as a system service.
To start or stop the Server with the Administrator
In the Administrator, connect
to the server, then click the Server
tab.
On the main menu, click Edit,
then click Service Applet Settings.
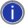
The Transfer Engine Service Settings dialog box appears.
Click Start
service (or Stop
service) and close the Transfer
Engine Service Settings dialog box.
|
|
If Install service
is the only button enabled in the Transfer
Engine Service Settings dialog box, click it, then click Start service. |
To start or stop the server using the Services option in
the Control Panel
Open the Windows Services
dialog box.
In the Name
column, click GlobalSCAPE Secure FTP
Server or GlobalSCAPE Secure FTP
Server (FIPS), then right-click it and click Start
(or Stop).
To start or stop the server from the command line
Click Start,
then click Run.
Enter cmd or
command.
Click OK.
To start the Server, at the prompt type:
Net start "globalscape secure ftp server"
(Include the quotation marks.)
To stop the Server, at the prompt type:
Net stop "globalscape secure ftp server"
(Include the quotation marks.)
After the service is started or stopped, type Exit.
|
|
Any time you run a server, you expose your computer to
outside users. There is the potential for exposing files and programs
on your computer and network to malicious outside users, particularly
if the Server is compromised.
Although you can set folder permissions from within the Server Administrator,
you can add an extra level of protection by establishing a user account
for the Server and then limiting folder access through the Server's user
account permissions. This establishes a stopgap until server/system integrity
can be restored if the Server is ever compromised. |
To configure the server to run securely
Create a user account for the server
Assign permissions
to this user account
Assign the server
to the account
Log the server on as a service
If
necessary, configure the server's user account to map
a virtual folder to a network drive.